Constellations
NakshatraNakshatra is the term for lunar mansion in Hindu astrology. A nakshatra is one of 27 (sometimes also 28) sectors along the ecliptic. Their names are related to the most prominent asterisms in the respective sectors.
The starting point for the nakshatras is the point on the ecliptic directly opposite to the star Spica called Chitrā in Sanskrit. It is called Meshādi or the “start of Aries”. The ecliptic is divided into each of the nakshatras eastwards starting from this point. The number of nakshatras reflects the number of days in a sidereal month, the width of a nakshatra traversed by the Moon in about one day. Each nakshatra is further subdivided into four quarters (or padas). These play a role in popular Hindu astrology, where each pada is associated with a syllable, conventionally chosen as the first syllable of the given name of a child born when the Moon was in the corresponding pada.
The nakshatras of traditional bhartiya astronomy are based on a list of 28 asterisms found in the Atharvaveda and also in the Shatapatha Brahmana. The first astronomical text that lists them is the Vedanga Jyotisha.
In classical Hindu scriptures (Mahabharata, Harivamsa), the creation of the nakshatras is attributed to Daksha. They are personified as daughters of the deity and as wives of Chandra, the Moon god, or alternatively the daughters of Kashyapa, the brother of Daksha.
Each of the nakshatras is governed as ‘lord’ by one of the nine graha in the following sequence: Ketu (South Lunar Node), Shukra (Venus), Ravi or Surya (Sun), Chandra (Moon), Mangala (Mars), Rahu (North Lunar Node), Guru or Brihaspati (Jupiter), Shani (Saturn) and Budha (Mercury). This cycle repeats itself three times to cover all 27 nakshatras. The lord of each nakshatra determines the planetary period known as the dasha, which is considered of major importance in forecasting the life path of the individual in Hindu astrology.
In Vedic Sanskrit, the term nákṣatra may refer to any heavenly body, or to “the stars” collectively. The classical concept of a “lunar mansion” is first found in the Atharvaveda, and becomes the primary meaning of the term in Classical Sanskrit.
Nakshatras in the Atharvaveda
In the Atharvaveda a list of 28 stars or asterisms is given, many of them corresponding to the later nakshatras:
(1) Kṛttikā (the Pleiads), (2) Rohinī, (3) Mrigashīrsha, (4) Ārdrā, (5) Punarvasu, (6) Sūnritā, (7) Pushya, (8) Bhanu (the Sun), (9) Asleshā, (10) Maghā, (11) Svāti (Arcturus), (12) Chitrā (Spica), (13) Phalgunis, (14) Hasta, (15) Rādhas, (16) Vishākhā, (17) Anurādhā, (18) Jyeshthā, (19) Mūla, (20) Ashādhas, (21) Abhijit, (22) Sravana, (23) Sravishthās, (24) Satabhishak, (25) Proshtha-padas, (26) Revati, (27) Asvayujas, (28) Bharani. Interestingly enough, the term “nakshatra” has a different meaning as demonstrated in the “Surya Siddhanta” which is an ancient text on astronomy. In the early chapters, the author, Mayasura or Mayan, describes various time units. He writes that a “prana” is a duration of 4 seconds. He then continues with a discussion of a number of time units with progressively long durations made up of the shorter time units all composed of a number of pranas. Amongst those time units are something he calls “nakshatra.” For example, there are 15 pranas in a minute; 900 pranas in an hour; 21600 pranas in a day, 583,200 pranas in a nakshatra (month). According to Mayan, a nakshatra is a time unit with a duration of 27 days. This 27 day time cycle has been taken to mean a particular group of stars. The relationship to the stars really has to do with the periodicity with which the Moon travels over time and through space past the field of the specific stars called nakshatras. Hence, the stars are more like numbers on a clock through which the hands of time pass (the moon). This concept that nakshatra means a time unit has been lost and diverted to meaning a set of stars in the sky. This concept was discovered by Dr. Jessie Mercay in her research on Surya Siddhanta. It is documented in a textbook called “Fundamentals of Mamuni Mayans Vaastu Shastras, Building Architecture of Sthapatya Veda and Traditional Indian architecture.”
List of Nakshatras
Position of the Hindu Nakshatra Mandala as per the coordinates specified in Surya Siddhantha
The classical list of 27 nakshatras is first found in the Vedanga Jyotisha, a text dated to the final centuries BCE. The nakshatra system predates the influence of Hellenistic astronomy on vedic tradition, which became prevalent from about the 2nd century CE.
In Hindu astronomy, there was an older tradition of 28 Nakshatras which were used as celestial markers in the heavens. When these were mapped into equal divisions of the ecliptic, a division of 27 portions was adopted since that resulted in a cleaner definition of each portion subtending 13° 20′ (as opposed to 12° 51 3/7’ in the case of 28 segments). In the process, the Nakshatra Abhijit was left out without a portion.[2]:179 The Surya Siddhantha concisely specifies the coordinates of the twenty seven Nakshatras[2]:211
The following list of nakshatras gives the corresponding regions of sky, following Basham
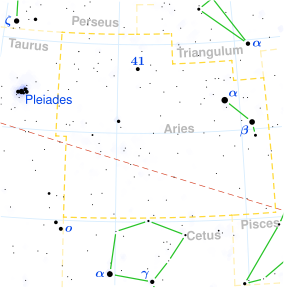
ASHWINI
| Position : | 00°00′ MES 13°20′ MES |
| Associated Stars : | β and γ Arietis |
| Personality Traits : | Liked by all, of fine appearance, intelligent, skilled in work, progressive, wealthy, self-willed, spends easily, helpful to friends, good adviser, has healing capacity. |
| Description : | Lord: Ketu (South lunar node) Symbol : Horse’s head,/li> Deity : Ashvins, the horse-headed twins who are physicians to the godsIndian zodiac : 0° – 13°20′ Mesha Western zodiac 26° Aries – 9°20′ Taurus |
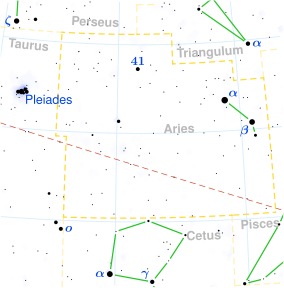
BHARANI
| “the bearer” | |
| Position : | 13°20′ MES 26°40′ MES |
| Associated Stars : | 35, 39, and 41 Arietis |
| Personality Traits : | Truthful, honest, intelligent, pure-hearted, dutiful, self-controled, of strong will-power, firm, forbearing, persevering, successful at work, popular, happy, generous. |
| Description : | Lord: Shukra (Venus) Symbol: Yoni, the female organ of reproduction Deity: Yama, god of death or Dharma Indian zodiac: 13° 20′ – 26°40′ Mesha Western zodiac 9° 20′ – 22° 40′ Taurus |
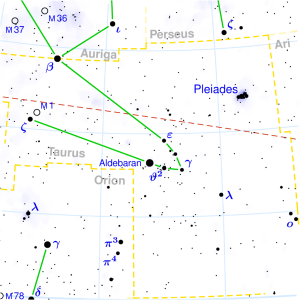
KRITTIKA
| an old name of the Pleiades; personified as the nurses of Kārttikeya, a son of Shiva. | |
| Position : | 26°40′ MES 10°00′ VRB |
| Associated Stars : | Pleiades |
| Personality Traits : | Dignified, strong, healthy, highly esteemed, famous, ambitious, performing monumental deeds, a good commander, happy, pure, loves good food. |
| Description : | Lord: Surya (Sun) Symbol: Knife or spear Deity : Agni, god of fire Indian zodiac: 26°40′ Mesha – 10° Vrishabha Western zodiac 22° 40′ Taurus – 6° Gemini |
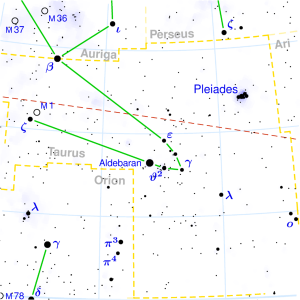
ROHINI
| “the red one”, a name of Aldebaran. Also known as brāhmī | |
| Position : | 10°00′ VRB 23°20′ VRB |
| Associated Stars : | Aldebaran |
| Personality Traits : | Of settled mind, religious, meditative, learned, lucky, non-covetous, philantropic, refined, has clean habits,of firm views, influential, a good guide, lovely in appearance. |
| Description : | Lord: Chandra (Moon) Symbol: Cart or chariot, temple, banyan tree Deity : Prajapati, the Creator Indian zodiac: 10° – 23°20′ Vrishabha Western zodiac 6° – 19°20′ Gemini |
MRIGASHIRA
| “the deer’s head”. Also known as āgrahāyaṇī | |
| Position : | 23°20′ VRB 06°40′ MIT |
| Associated Stars : | λ, φ Orionis |
| Personality Traits : | Full of love, motherly, cheerful,sincere, simple, of active habits, adaptable, good memory, persevering,good conversationalist, good in research, investigating, not showing his weak side. |
| Description : | Lord: Mangala (Mars) Symbol: Deer’s head Deity: Soma, Chandra, the Moon god Indian zodiac: 23° 20′ Vrishabha – 6° 40′ Mithuna Western zodiac: 19°20′ Gemini – 2°40′ Cancer |
ARDRA
| “the moist one” | |
| Position : | 06°40′ MIT 20°00′ MIT |
| Associated Stars : | Betelgeuse |
| Personality Traits : | Assertive, strong willed, sincere in work, ambitious, successful in commerce, of high self-esteem, sensative,good psychological insight, cool, versatile, knowledgeable. |
| Description : | Lord: Rahu (North lunar node) Symbol: Teardrop, diamond, a human head Deity : Rudra, the storm god Indian zodiac: 6° 40′ – 20° Mithuna Western zodiac: 2° 40′ – 16° Cancer |
PUNARVASU
| “the two restorers of goods”, also known as yamakau “the two chariots” | |
| Position : | 20°00′ MIT 03°20′ KAR |
| Associated Stars : | Castor and Pollux |
| Personality Traits : | Well-behaved, truthful, virtuous, self-controled, humble, compassionate, amiable, diligent, clever, enthusiastic,easily contented, makes many journeys. |
| Description : | Lord: Guru (Jupiter) Symbol : Bow and quiver Deity : Aditi, mother of the gods Indian zodiac: 20° Mithuna – 3°20′ Karka Western zodiac 16° – 29°20′ Cancer |
PUSHYAMI
| “the nourisher”, also known as sidhya or tiṣya | |
| Position : | 03°20′ KAR 16°40′ KAR |
| Associated Stars : | γ, δ and θ Cancri |
| Personality Traits : | Soft-hearted, honest, intelligent, intuitive, learned in shastras, balanced, prosperous, charitable, popular, fond of travel, self-reliant, holds a commanding position. |
| Description : | Lord: Shani (Saturn) Symbol : Cow’s udder, lotus, arrow and circle Deity : Bṛhaspati, priest of the gods Indian zodiac: 3°20′ -16°40′ Karka Western zodiac 29°20′ Cancer – 12°40′ Leo |
ASHLESHA
| “the embrace” | |
| Position : | 16°40′ KAR 00°00′ SIM |
| Associated Stars : | δ, ε, η, ρ, and σ Hydrae |
| Personality Traits : | Straightforward, smart, of penetrating vision, independent, ambitious, bright speaker, commanding respect, skilled in politics, diplomatic, good in keeping secrets, loves travel. |
| Description : | Lord: Budha (Mercury) Symbol: Serpent Deity : Sarpas or Nagas, deified snakes Indian zodiac: 16°40′ – 30° Karka Western zodiac 12°40′ – 26° Leo |
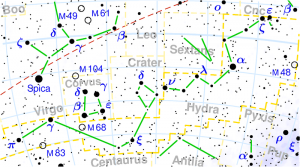
MAGHA
| “the bountiful” | |
| Position : | 00°00′ SIM 13°20′ SIM |
| Associated Stars : | Regulus |
| Personality Traits : | Royal, dignified, self-assured,outspoken, assertive, doing important works, praiseworthy, rich, generous,altruistic, devout, respecting elders, artistic. |
| Description : | Lord: Ketu (south lunar node) Symbol : Royal Throne Deity : Pitrs, ‘The Fathers’, family ancestors Indian zodiac: 0° – 13°20′ Simha Western zodiac 26° Leo – 9°20′ Virgo |
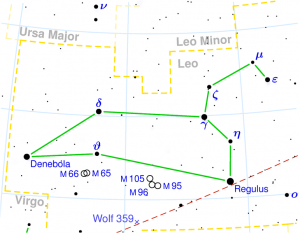
PURVA PHALGUNI
| “first reddish one” | |
| Position : | 13°20′ SIM 26°40′ SIM |
| Associated Stars : | δ and θ Leonis |
| Personality Traits : | Prosperous, liberal in gifts, good in business, loves freedom, always travelling, famous, respected, sweet-tongued, artistic, of bright appearance, majestic, victorious. |
| Description : | Lord: Shukra (Venus) Symbol : Front legs of bed, hammock, fig tree Deity : Aryaman, god of patronage and favours Indian zodiac: 13°20′ – 26°40′ Simha Western zodiac 9°20′ – 22°40′ Virgo |
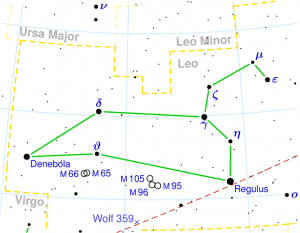
UTTARA PHALGUNI
| “second reddish one” | |
| Position : | 26°40′ SIM 10°00′ KAN |
| Associated Stars : | Denebola |
| Personality Traits : | Intellectual, learned, religious,sincere, good teacher, loved by all, helpful, hospitable, good patron, neat behaviour, lives in comfort. |
| Description : | Lord: Surya (Sun) Symbol: Four legs of bed, hammock Deity : Bhaga, god of marital bliss and prosperity Indian zodiac: 26°40′ Simha- 10° Kanya Western zodiac 22°40′ Virgo – 6° Libra |
HASTA
| “the hand” | |
| Position : | 10°00′ KAN 23°20′ KAN |
| Associated Stars : | α, β, γ, δ and ε Corvi |
| Personality Traits : | Enthousiastic, resourceful, industrious, determined, persevering, knowledgeable, contemplative, witty, good adviser,calm, of sweet smiles. |
| Description : | Lord: Chandra (Moon) Symbol: Hand or fist Deity : Savitr, the Sun god Indian zodiac: 10° – 23°20′ Kanya Western zodiac 6° – 19°20′ Libra |
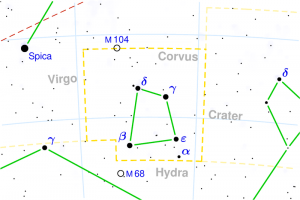
CHITRA
| “the bright one”, a name of Spica | |
| Position : | 23°20′ KAN 06°40′ TUL |
| Associated Stars : | Spica |
| Personality Traits : | Very intelligent, intuitive, artistic, good designer, purposeful, enterprising, skilled in organizing, good conversationalist, loves ornaments. |
| Description : | Lord: Mangala (Mars) Symbol: Bright jewel or pearl Deity : Indra, chief of the gods Indian zodiac: 23°20′ Kanya – 6°40′ Tula Western zodiac: 19°20′ Libra – 2°40′ Scorpio |
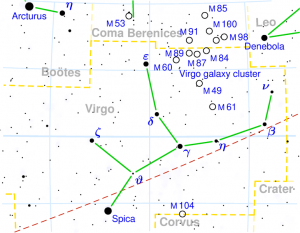
SWATI
| “Su-Ati (sanskrit) Very good” name of Arcturus | |
| Position : | 06°40′ TUL 20°00′ TUL |
| Associated Stars : | Arcturus |
| Personality Traits : | Composed, modest, merciful, sympathetic, of sweet speech, intuitive, of sound judgement, scholarly, self-controled, self-willed, independent, makes many journeys, skilled in trade, charitable. |
| Description : | Lord: Rahu (north lunar node) Symbol: Shoot of plant, coral Deity : Vayu, the Wind god Indian zodiac: 6°40′ – 20° Tula Western zodiac 2°40′ – 16° Scorpio |
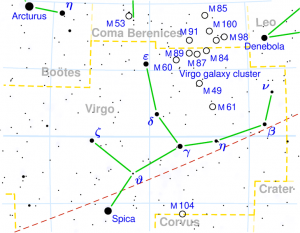
VISHAKHA
| “forked, having branches”; also known as rādhā “the gift” | |
| Position : | 20°00′ TUL 03°20′ VRK |
| Associated Stars : | α, β, γ and ι Librae |
| Personality Traits : | Energetic, purposeful, aiming at success, very intelligent, good and distinct speech, courteous, loves company, moves in high and low circles, good politician. |
| Description : | Lord: Guru (Jupiter) Symbol : Triumphal arch, potter’s wheel Deity : Indra, chief of the gods; Agni, god of Fire Indian zodiac: 20° Tula – 3°20′ Vrishchika Western zodiac 16° – 29°20′ Scorpio |
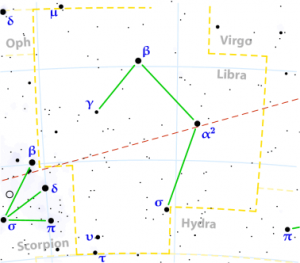
ANURADHA
| “following rādhā” | |
| Position : | 03°20′ VRK 16°40′ VRK |
| Associated Stars : | β, δ and π Scorpionis |
| Personality Traits : | Devoted, loving, friendly, optimistic, determined, progressive, has strong appetite, hard working, wealthy, honourable, contemplative, makes many journeys. |
| Description : | Lord: Shani (Saturn) Symbol : Triumphal archway, lotus Deity : Mitra, one of Adityas of friendship and partnership Indian zodiac: 3°20′ – 16°40′ Vrishchika Western zodiac 29°20′ Scorpio – 12°40′ Sagittarius |
JYESHTA
| “the eldest, most excellent” | |
| Position : | 16°40′ VRK 00°00′ DHA |
| Associated Stars : | α, σ, and τ Scorpionis |
| Personality Traits : | Joyful, good natured, irreproachable, religious, learned, poetical, sober, sharp eyed, skilled, self-made, independent, loves freedom, famous, wealthy, good leader. |
| Description : | Lord: Budha (Mercury) Symbol : circular amulet, umbrella, earring Deity : Indra, chief of the gods Indian zodiac: 16°40′ – 30° Vrishchika Western zodiac 12°40′ – 26° Sagittarius |
MOOLA
| “the root” | |
| Position : | 00°00′ DHA 13°20′ DHA |
| Associated Stars : | ε, ζ, η, θ, ι, κ, λ, μ and ν Scorpionis |
| Personality Traits : | High self-esteem, dignified, wide awake, clever, of firm views, goes for basic and original things, straightforward, law-abiding, generous, non-injurous, very special. |
| Description : | Lord: Ketu (south lunar node) Symbol : Bunch of roots tied together, elephant goad Deity : Pitrs, ‘The Fathers’, family ancestors Indian zodiac: 0° – 13°20′ Dhanus Western zodiac 26° Sagittarius – 9°20′ Capricorn |
PURVA ASHADHA
| “first of the aṣāḍhā”, aṣāḍhā “the invincible one” being the name of a constellation | |
| Position : | 13°20′ DHA 26°40′ DHA |
| Associated Stars : | δ and ε Sagittarii |
| Personality Traits : | Farseeing, wise, humane, forgiving, protective, generous, firm in danger, enterprising, influential, unyielding, victorious, loves travel. |
| Description : | Lord: Shukra (Venus) Symbol: Elephant tusk, fan, winnowing basket Deity : Apah, god of Water Indian zodiac: 13°20′ – 26°40′ Dhanus Western zodiac 9°20′ – 22°40′ Capricorn |
UTTARA ASHADHA
| “second of the aṣāḍhā” | |
| Position : | 26°40′ DHA 10°00′ MAK |
| Associated Stars : | ζ and σ Sagittarii |
| Personality Traits : | Popular, famous, humorous, wise, virtuous, peace-loving, grateful, trustworthy, a good adviser, observing penance, methodical, penetrating, intensive, victorious. |
| Description : | Lord: Surya (Sun) Symbol : Elephant tusk, small bed Deity : Visvedevas, universal gods Indian zodiac: 26°40′ Dhanus – 10° Makara Western zodiac 22°40′ Capricorn – 6° Aquarius |
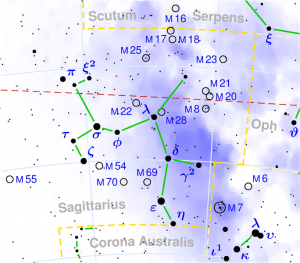
SHRAVANA
| Position : | 10°00′ MAK 23°20′ MAK |
| Associated Stars : | α, β and γ Aquilae |
| Personality Traits : | Scholarly, wise, respecting the shastras, good educator, peaceful, large-hearted, enthusiastic, active, versatile, progressive, circumspective, famous, loves adornment. |
| Description : | Lord: Chandra (Moon) Symbol : Ear or Three Footprints Deity : Vishnu, preserver of universe Indian zodiac: 10° – 23°20′ Makara Western zodiac 6° – 19°20′ Aquarius |
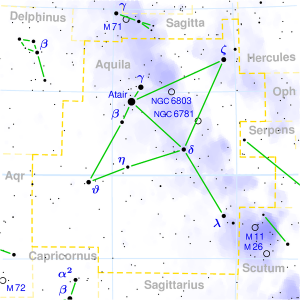
DHANISHTA
| “most famous”, also Shravishthā “swiftest” | |
| Position : | 23°20′ MAK 06°40′ KUM |
| Associated Stars : | α to δ Delphini |
| Personality Traits : | Fearless, ambitious, self-willed, has controling capacity, high self-esteem, lucky, has Midas touch, lives in luxuries, generous, fond of music, loves society, scientific. |
| Description : | Lord: Mangala (Mars) Symbol : Drum or flute Deity : Eight vasus, deities of earthly abundance Indian zodiac: 23°20′ Makara – 6°40′ Kumbha Western zodiac 19°20′ Aquarius – 2°40′ Pisces |
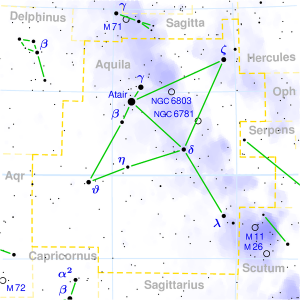
SHATABHISHA
| “Comprising a hundred physicians” | |
| Position : | 06°40′ KUM 20°00′ KUM |
| Associated Stars : | γ Aquarii |
| Personality Traits : | Tactful, truthful, learned, good memory, meditative, philosophical, prefers solitude, independent, clever, uncompromising, powerful, acting fast, has healing capacity. |
| Description : | Lord: Rahu (north lunar node) Symbol : Empty circle, 1,000 flowers or stars Deity : Varuna, god of celestial waters Indian zodiac: 6°40′ – 20° Kumbha ; Western zodiac 2°40′ – 16° Pisces |
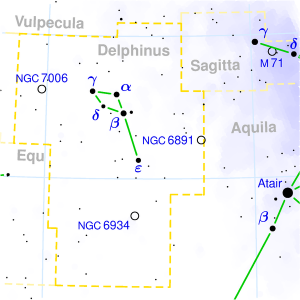
PURVA BHADRAPADA
| “the first of the blessed feet” | |
| Position : | 20°00′ KUM 03°20′ MEE |
| Associated Stars : | α and β Pegasi |
| Personality Traits : | Serious, learned, of distinct speech, humane, honest, helpful, a good friend, impartial, unselfish, skilled in earning money, principled, polite, observing penance. |
| Description : | Lord: Guru (Jupiter) Symbol : Swords or two front legs of funeral cot, man with two faces Deity : Ajikapada, an ancient fire dragon Indian zodiac: 20° Kumbha – 3°20′ Meena ; Western zodiac 16° – 29°20′ Pisces |
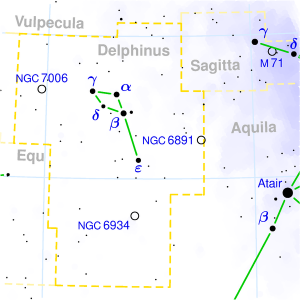
UTTARA BHADRAPADA
| “the second of the blessed feet” | |
| Position : | 03°20′ MEE 16°40′ MEE |
| Associated Stars : | γ Pegasi and α Andromedae |
| Personality Traits : | Virtuous, happy, knowledgeable, wise, able speaker, pure-hearted, aimiable, diligent, prosperous, strong personality, victorious, loves renunciation. |
| Description : | Lord: Shani (Saturn) Symbol : Twins, back legs of funeral cot, snake in the water Deity : Ahir Budhyana, serpent or dragon of the deep Indian zodiac: 3°20′ – 16°40′ Meena ; Western zodiac 29°20′ Pisces – 12°40′ Aries |
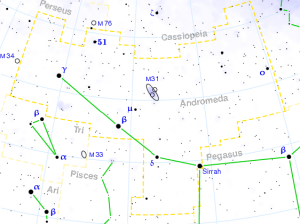
REVATI
| “prosperous” | |
| Position : | 16°40′ MEE 00°00′ MES |
| Associated Stars : | ζ Piscium |
| Personality Traits : | Sympathetic, sensative, intuitive, spiritual, soft-spoken, happy, popular, independent, dutiful, orthodox, rich, philantropic, leaves no room for blame. |
| Description : | Lord: Budha (Mercury) Symbol : Fish or a pair of fish, drum Deity : Pushan, nourisher, the protective deity Indian zodiac: 16°40′ – 30° Meena Western zodiac 12°40′ – 26° Aries |
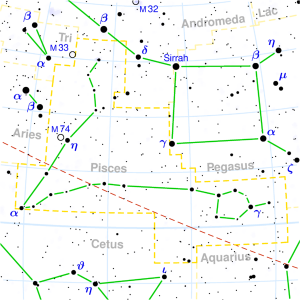
MES=Mesha, VRB=Vrishabha, MIT=Mithuna, KAR=Karka, SIM=Simha, KAN=Kanya, TUL=Tula, VRK=Vrishcika, DHA=Dhanu, MAK=Makara, KUM=Kumbha, MEE=Meena.
Padas (quarters)
Each of the 27 Nakshatras cover 13°20’ of the ecliptic each. Each Nakshatra is also divided into quarters or padas of 3°20’, and the below table lists the appropriate starting sound to name the child. The 27 nakshatras, each with 4 padas, give 108, which is the number of beads in a japa mala, indicating all the elements (ansh) of Vishnu:
| Name | Pada 1 | Pada 2 | Pada 3 | Pada 4 |
| Ashwini (अश्विनि) | चु Chu | चे Che | चो Cho | ला La |
| Bharani (भरणी) | ली Li | लू Lu | ले Le | लो Lo |
| Kritika (कृत्तिका) | अ A | ई I | उ U | ए E |
| Rohini(रोहिणी) | ओ O | वा Va/Ba | वी Vi/Bi | वु Vu/Bu |
| Mrigashīrsha(म्रृगशीर्षा) | वे Ve/Be | वो Vo/Bo | का Ka | की Ke |
| Ārdrā (आर्द्रा) | कु Ku | घ Gha | ङ Ng/Na | छ Chha |
| Punarvasu (पुनर्वसु) | के Ke | को Ko | हा Ha | ही Hi |
| Pushya (पुष्य) | हु Hu | हे He | हो Ho | ड Da |
| Āshleshā (आश्लेषा) | डी Di | डू Du | डे De | डो Do |
| Maghā (मघा) | मा Ma | मी Mi | मू Mu | मे Me |
| Pūrva or Pūrva Phalgunī (पूर्व फाल्गुनी) | नो Mo | टा Ta | टी Ti | टू Tu |
| Uttara or Uttara Phalgunī (उत्तर फाल्गुनी) | टे Te | टो To | पा Pa | पी Pi |
| Hasta (हस्त) | पू Pu | ष Sha | ण Na | ठ Tha |
| Chitra (चित्रा) | पे Pe | पो Po | रा Ra | री Ri |
| Svātī (स्वाति) | रू Ru | रे Re | रो Ro | ता Ta |
| Viśākhā (विशाखा) | ती Ti | तू Tu | ते Te | तो To |
| Anurādhā (अनुराधा) | ना Na | नी Ni | नू Nu | ने Ne |
| Jyeshtha (ज्येष्ठा) | नो No | या Ya | यी Yi | यू Yu |
| Mula (मूल) | ये Ye | यो Yo | भा Bha | भी Bhi |
| Pūrva Ashādhā (पूर्वाषाढ़ा) | भू Bhu | धा Dha | फा Bha/Pha | ढा Dha |
| Uttara Aṣāḍhā (उत्तराषाढ़ा) | भे Bhe | भो Bho | जा Ja | जी Ji |
| Śrāvaṇa (श्रावण) | खी Ju/Khi | खू Je/Khu | खे Jo/Khe | खो Gha/Kho |
| Śrāviṣṭha (श्रविष्ठा) or Dhanishtha (धनिष्ठा) | गा Ga | गी Gi | गु Gu | गे Ge |
| Shatabhisha (शतभिषा)or Śatataraka | गो Go | सा Sa | सी Si | सू Su |
| Pūrva Bhādrapadā (पूर्वभाद्रपदा) | से Se | सो So | दा Da | दी Di |
| Uttara Bhādrapadā (उत्तरभाद्रपदा) | दू Du | थ Tha | झ Jha | ञ Da/Tra |
| Revati (रेवती) | दे De | दो Do | च Cha | ची Chi |
Hindu given names
Hindu astrologers (see Jyotisha) teach that when a child is born, they should be given an auspicious first name which will correspond to the child’s Nakshatra. The technique for deducing the name is to see which nakshatra the Moon is in at the moment of birth; this gives four possible sounds. A refinement is to pick one sound out of that four that relates to the Pada or division of the Nakshatra. Each Nakshatra has four Padas and four sounds and each Pada is of equal width. The Moon remains in each Nakshatra for approximately one day.
A further refinement or opportunity is to instead use the Nakshatra that the ascendent resides in at birth. The same broad choice of sounds and Padas apply, but now the sounds change roughly every 15 minutes. The ascendent passes through all 27 Nakshatras every 24 hours, being in each one for 53 and a third minutes of time, and is in a Pada for 13 and a third minutes of time. By using the ascendent’s nakshatra, instead of the Moon’s nakshatra leads more to comfort of the Self, rather than comfort of the mother. This second approach is only really applicable if intuitively the Moon approach does not feel right.
Electional astrology
Constellations are grouped on the basis of their nature, type of their face, degree of their beneficence, their quarters in different signs, with reference to the constellation occupied by the Sun, with reference to the birth constellation (Janma Nakshatra), their caste, etc. The current constellation occupied by the Moon, and its nature forms the fundamental of Vedic system of electional astrology (Muhurta). Some of the activities and works which are associated with the Nakshatras are given below based on their fundamental nature:
- Fixed (Dhruva, Sthira) constellations : Rohini, Uttara Bhādrapadā, Uttra Falguni, and Uttara Ashada
Fixed and permanent nature, house, village, temple, entering in new hose-city-temple, religious works, rites for getting peace, propitiation of portents, Vinayaka Shanti, coronation, sowing of seeds, planting of small garden, starting of vocal music, friendship, sexual works, making & wearing of ornaments & clothes may be auspiciously begun / effectively performed. Works allocated to delicate & friendly (Mridu) asterisms may also be performed. - Movable (Chala , Chara) constellations : Punarvasu, Swaati, Sharavana, Shatabhishā & Shravishthā
Related to motion & movement, riding on a vehicle or elephant, opening of shop, walking first time, walking in garden, sex, making jewellery, learning of a trait. Things performed in Small (Laghu) constellation are also effectively performed in the Movable constellations. - Cruel (Ugra, Karur) constellations : Magha, Bharani, Porva Palguni, Poorva Shada, & Poorva Bhadra.
Ambush, burning, poisoning (self & others), making & using weapons especially related to fire, cheating / deception / wickedness / craftiness, cutting & destroying, controlling of animals, beating & punishing of enemy. Works allocated to Sharp / Horrible (Darun) asterisms are also successfully done in these asterisms. - Mixed (Mishra & Sadharan) constellations : Vishakha & Krittika.
Fire works, burning of sacred fire (Agnihotra), using poison, fearsome works, arresting, adulteration (mixing), donation of ox to get one’s desires fulfilled (Vrashotsarga). Works prescribed under cruel (Ugra, Karur) constellations may also be performed. As per N.S. works of Sweet / delicate & friendly (Mridu & Maitri) constellations can also be included. - Small (Laghu & Kshipra) constellations : Hasta, Abhijit, Pushya, and Ashvini.
Selling, medical knowledge, using & handling of medicines, literature-music-art, the 64 Kala Shilpa (various arts, sculpture etc.) jewellery making & wearing, sexual intercourse. And the works prescribed for Movable (Char) constellations. Though Abhijit is included in Small group of asterisms, but is rarely referred in the Muhurt prescriptions. - Sweet/Delicate & Friendly (Mridu & Maitri) constellations : Mrigashīrsha, Chitra, Anuradha and Revati.
Starting & learning singing of songs, clothes & jewellery making & wearing, Manglik works, matter related to friends, female company, enjoyments, sexual passions. - Sharp & Horrible ( Teekshan & Darun ) constellations : Jyeshta, Ardra, Ashlesha, and Moola
Charm or spell causing disease or death, hypnotism, sorcery; ghost, ambush, horror, murder, capture, matters related to secrecy, backbiting, starting of quarrel, separation, matters related to friendship & breaking thereof, training & tying of animals, pleasure works, playing games, getting made & wearing of new dress & ornaments, starting & learning singing of songs, entering into village / city, peaceful & developmental works.
